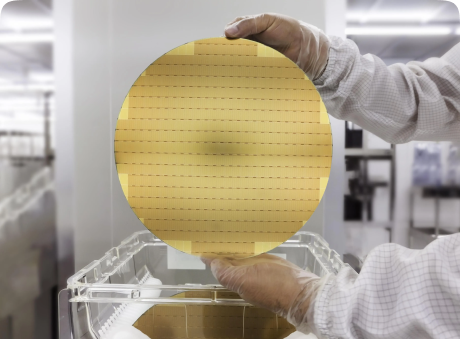
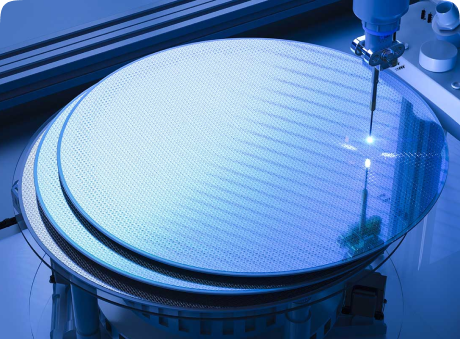
Our Products
Our Premium Wafers
High-quality wafer materials crafted to support advanced, high-performance semiconductor applications globally.
GaAs Wafers
Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) wafers are critical components in modern electronics and photonics due to their superior electrical and optical properties.
Here’s a focused overview:
GaAs’ is shorthand for Gallium Arsenide, a compound made up of two elements, and the semiconductor used to manufacture GaAs wafers. GaAs is used as a direct bandgap semiconductor, which in layman’s terms, simply means that particles such as electrons can pass through components much quicker and with very little interference. This makes them particularly useful in optical devices because photons, the basic unit for all light, can pass through lenses with ease.
What are GaAs Wafers Use For?
The use of GaAs wafers is dictated by the capabilities of the compound. Because GaAs is a direct bandgap semiconductor, it is especially useful in sensitive electronic equipment that requires amplifying low frequencies. Some of the most common applications for GaAs wafers include:
-
Radars
-
Radio communication equipment
-
Tachometers
-
Satellites
-
Microwave
-
LEDs
Key Properties of GaAs Wafers
High Electron Mobility:
-
Allows faster signal transmission compared to silicon, enabling high-speed applications.
Direct Bandgap:
-
Ideal for optoelectronic devices like LEDs and laser diodes due to efficient light emission.
Wide Bandgap:
-
Enables operation at high voltages and temperatures, making it robust in demanding environments.
Thermal and Radiation Resistance:
-
Performs well under high-temperature and high-radiation conditions, suitable for aerospace and military applications.
Low Noise Characteristics:
-
Ensures superior performance in communication and radar systems.
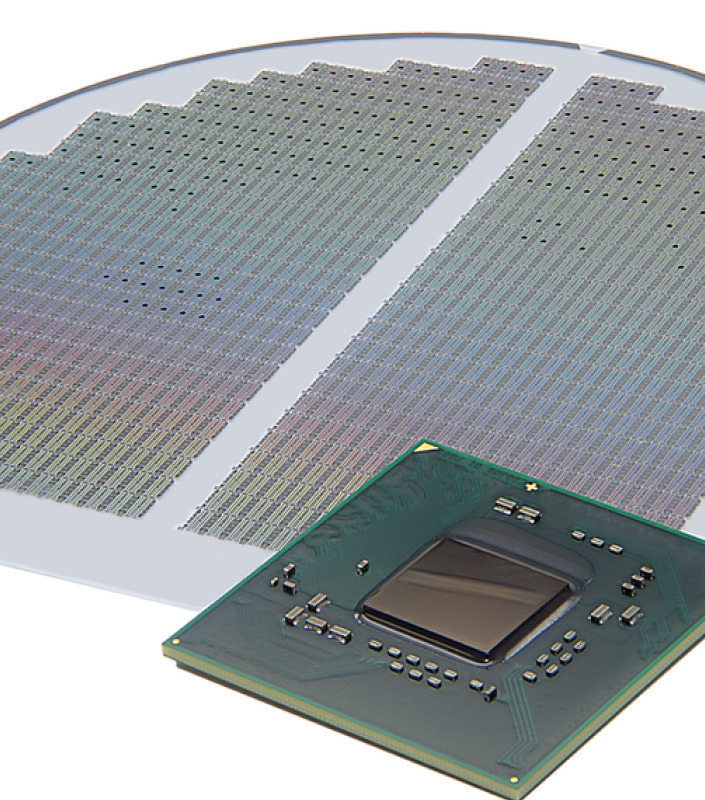
Applications of GaAs Wafers
Optoelectronics:
-
-
Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs): High brightness and efficiency.
-
Laser Diodes: Used in fiber optics, LiDAR, and optical communication.
-
Photovoltaic Cells: High-efficiency solar cells, particularly for space applications.
-
High-Frequency Electronics:
-
-
Devices like HEMTs (High Electron Mobility Transistors) and MESFETs (Metal-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors) for 5G, satellite communication, and radar systems.
-
Power Electronics:
-
-
Enables compact, efficient power amplifiers and switches.
-
Photodetectors and Imaging:
-
-
Infrared sensors and detectors for spectroscopy, cameras, and remote sensing.
-
Aerospace and Defense:
-
-
GaAs is commonly used in radiation-resistant electronics and high-frequency communication systems.
-
Standard Specifications
-
Diameters: Common sizes are 2-inch, 3-inch, 4-inch, and sometimes 6-inch.
-
Crystal Orientation: Usually (100) or (111) planes, depending on the intended application.
-
Doping:
-
n-Type: Doped with silicon or tin.
-
p-Type: Doped with zinc or beryllium.
-
-
Thickness: Typically ranges from 200 µm to 700 µm.
-
Polishing: Available as single-side polished (SSP) or double-side polished (DSP).
Our Blogs
Industry Insights
Stay informed with the latest trends, innovations, and expert articles
in semiconductor wafer technology.
Sustainable Practices in Wafer Manufacturing
How Wafer Quality Impacts Performance
The Future of Semiconductor Wafers
Subscribe Newsletter
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Stay updated on the latest industry trends, product innovations, and exclusive offers.
Sign up today!
 sales@semiconductorus.com
sales@semiconductorus.com (201) 776-4282
(201) 776-4282